Introduction

Urethane casting is a common low-cost rapid prototyping method, widely used in small batch production and functional validation. Compared to traditional injection molding, its mold cycle is shorter, making it ideal for early-stage product iteration. For projects with frequent design changes, urethane casting offers unmatched flexibility.
For complex or functional plastic parts, urethane casting delivers realistic performance simulations without major investment. By using this method, design teams can quickly test product performance and save substantial mold costs.
Where Are Its Limits?

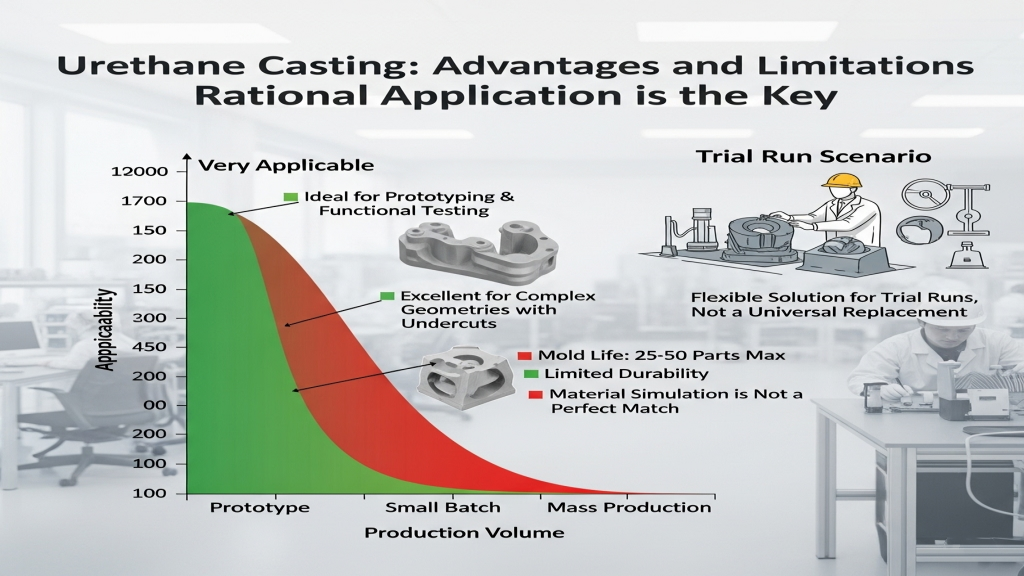
Urethane casting serves as a critical bridge between prototyping and low-volume production. It replicates intricate structures effectively, but its mold strength and service life are limited. This method is better suited for validation stages rather than long-term production.
- Ideal Phase: Prototyping stage: Perfect for early design and functional testing.
- Complex Geometry: Capable of replicating undercuts and detailed surfaces.
- Mold Life: Limited durability, usually supports up to 25–50 parts.
- Material Simulation: Mimics engineering-grade plastics to a certain degree.
😊 A flexible solution for trial runs, but not a universal replacement.
Is It Cost Effective?
Compared to injection molding, urethane casting eliminates the need for metal molds, dramatically cutting upfront tooling costs. It's particularly advantageous for batches between 10–100 units. For budget-sensitive and time-critical projects, urethane casting offers excellent value.
- Low Entry Cost: Ideal for low-budget projects
- No Steel Tooling: Silicone molds significantly reduce investment.
- Efficient for Small Runs: Most cost-effective below 100 parts.
- Quick Feedback Loop: Accelerates design iteration.
💰 Reduces tooling costs but not ideal for long-term scaling.
How Accurate Is It?

Though made from silicone molds, urethane casting provides excellent detail reproduction and dimensional consistency—especially in early runs. As mold wear increases, dimensional shifts become more noticeable. The first few parts often match injection-molded quality.
- High Initial Precision: Near-injection quality in early parts
- Mold Degradation: Dimensional accuracy declines over time.
- Surface Finish Control: Capable of replicating textures and gloss.
- Visual Prototypes: Suitable for presentation models.
🔍 High part quality at first—but lifespan must be tracked.
Urethane Casting vs Other Methods
| Process | Initial Cost | Lead Time | Surface Finish | Mold Life | Accuracy | Cost Range | Best Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urethane Casting | Low | Fast | High | 25–50 cycles | Medium-High | Small-volume | Validation |
| Injection Molding | High | Slow | High | 10,000+ | High | Medium/Large run | Mass Production |
| CNC Machining | Medium | Medium | Medium | No mold | High | Single/Functional | Prototype |
| 3D Printing | Low | Fast | Medium | No mold | Medium | Custom/Concept | Concept Testing |
What to Choose When
The choice between urethane casting and injection molding depends on budget, production volume, and development stage. While casting works best in early development, injection molding is essential for consistent large-scale output. Urethane casting fills the gap between 3D printing and traditional tooling.
1.Budget Constraints: Urethane casting wins for limited budgets.
2.Project Agility: Best for quick iterations and fast changes.
3.Functional Tests: Great for high-fidelity prototyping.
4.Final Usage: Go for injection molding when scaling up is required.
Conclusion
Urethane casting is not a one-size-fits-all method, but it excels during prototyping and validation. Its rapid turnaround and low entry cost make it an agile solution for modern development cycles. As a bridge between concept and production, it offers unique value in fast-paced markets.
For expert assistance in implementing for your production needs, visit our resource center or contact us. Let’s help you scale up your manufacturing with precision and efficiency!