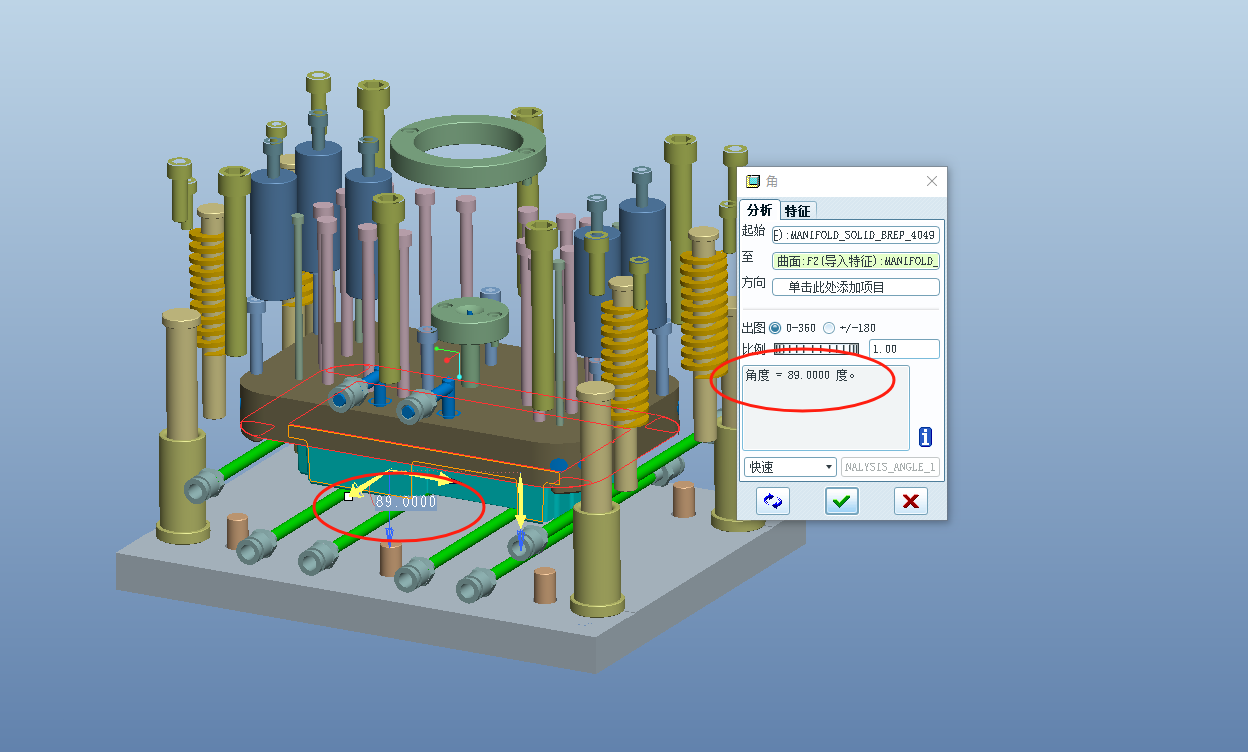
Draft angles play a crucial role in the injection molding process, facilitating the smooth ejection of parts from the mold and ensuring high-quality results. A draft angle is a slight taper added to the vertical walls of a molded part to reduce friction during ejection. Without a proper draft angle, parts may stick to the mold, leading to defects or damage.
Let’s dive into the importance of draft angle and how they improve part quality and manufacturing efficiency.
Why Are Draft Angles Necessary?
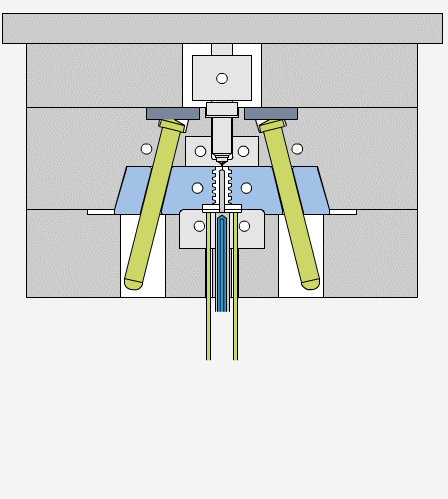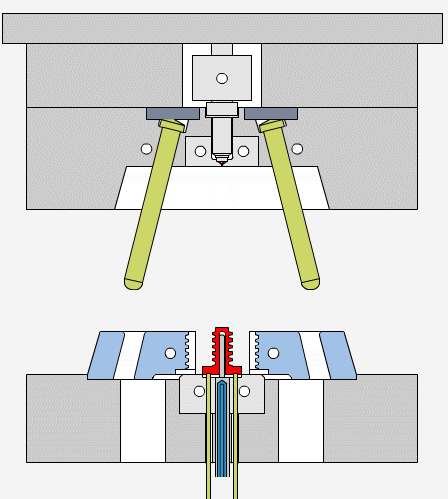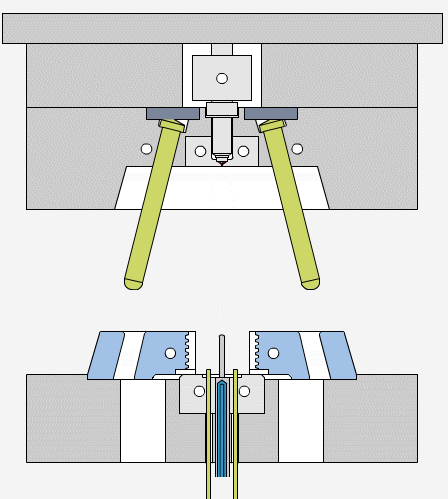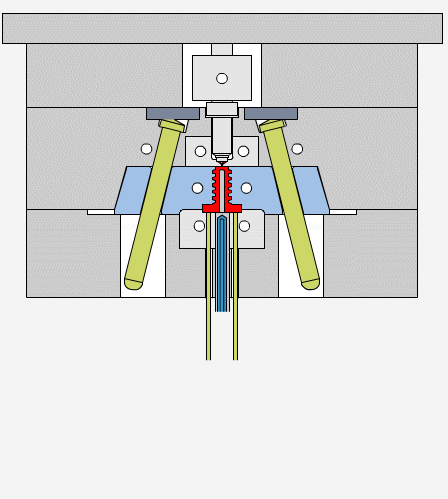
Draft angles allow molded parts to release easily from the mold cavity, reducing friction and the risk of damage. During cooling, the plastic material shrinks and grips the mold walls tightly. Without draft angles, parts may stick, causing ejection problems or surface defects like scratches and drag marks.
Draft angles also help maintain the structural integrity of parts by preventing unnecessary stress during ejection, which is especially important for intricate or thin-walled designs.
How Do Draft Angles Affect Part Quality?
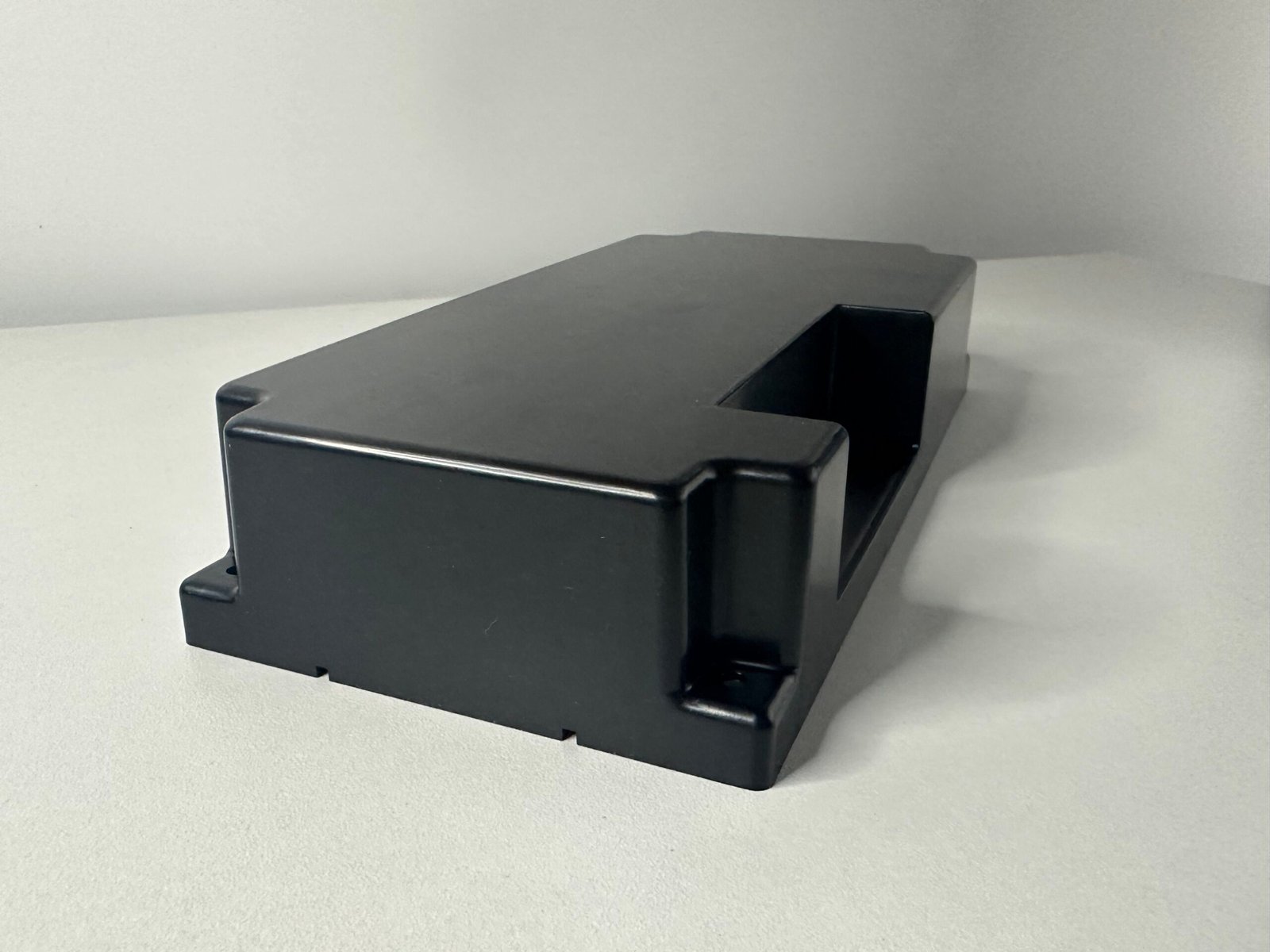

Well-designed draft angles improve the part's surface finish and dimensional accuracy. By allowing a smooth release, draft angles minimize surface imperfections caused by sticking or friction. For textured surfaces, draft angles are even more critical, as they prevent the texture from being damaged during ejection.
Parts with insufficient draft angles often require additional post-processing to remove surface defects, adding time and cost to the production process.
Best Practices for Designing Draft Angles

To ensure optimal results, follow these best practices for designing draft angles:
- Standard Angle: Use a draft angle of at least 1° per side for smooth surfaces. Increase this to 3°–5° for textured or rough surfaces.
- Material Considerations: Adjust draft angles based on the material's shrinkage rate. For example, materials like ABS may require greater draft angles than PP due to their higher shrinkage.
- Avoid Vertical Walls: Replace perfectly vertical walls with slightly tapered ones to reduce sticking during ejection.
Comparison of Draft Angle Recommendations
| Surface Type | Recommended Draft Angle |
|---|---|
| Smooth Surface | 1°–2° |
| Lightly Textured Surface | 2°–3° |
| Deep or Heavy Texture | 5° or more |
How Do Draft Angles Impact Mold Longevity?
Draft angles reduce wear and tear on the mold by minimizing ejection force. Parts that stick to the mold during ejection place additional stress on the mold and ejector system, leading to premature wear. Proper draft angles ensure smoother ejection, extending the lifespan of the mold and reducing maintenance costs.
Key Tips for Applying Draft Angles
- Consider Surface Finish: Increase draft angles for textured or rough surfaces to avoid damage during ejection.
- Account for Material Shrinkage: Higher shrinkage materials require larger draft angles for smooth ejection.
- Validate with Simulation: Use injection molding simulation tools to verify draft angle effectiveness before production.
- Design for Ejection Efficiency: Incorporate draft angles into all vertical walls to prevent sticking and reduce cycle times.
Conclusion
Draft angles are essential for ensuring smooth part ejection, protecting mold integrity, and improving part quality in injection molding. By optimizing draft angles based on material properties and surface finish, manufacturers can prevent defects, enhance efficiency, and extend mold life.
For expert advice on incorporating draft angles into your designs or improving your injection molding processes, visit our resource center or contact us. Let’s help you create high-quality parts with precision and efficiency!







