Introduction
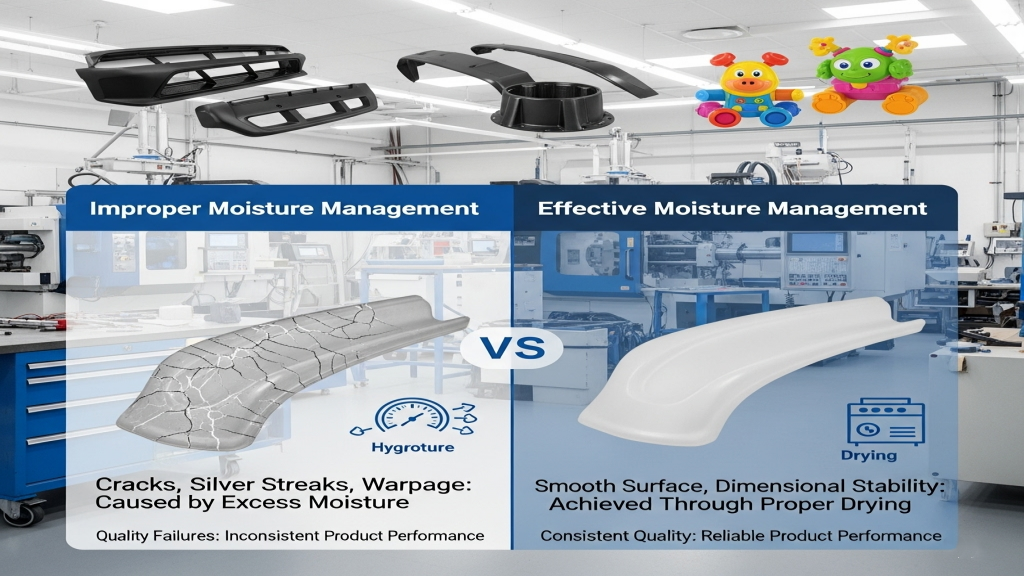
ABS is widely used in injection molding due to its excellent properties, yet its water absorption is often overlooked. Environmental humidity and processing conditions can silently trigger quality issues. Neglecting moisture management is often the root cause of quality failures.
In high-precision products, even trace moisture can lead to cracks, silver streaks, or warpage. Understanding ABS's hygroscopicity is essential for consistent, high-quality production.
What performance issues does ABS water absorption cause?

During injection, the absorbed moisture in ABS turns into vapor, forming bubbles and surface defects. Moist material reduces impact strength and mechanical integrity. Thicker parts are more prone to stress cracking due to internal moisture.
- Appearance defects: silver streaks, haze, pinholes
- Mechanical strength loss: polymer chains break down under moisture
- Dimensional instability: unpredictable expansion or shrinkage
- Post-processing issues: bonding and coating failures
💧 Moisture-contaminated ABS affects not only function but also production yield
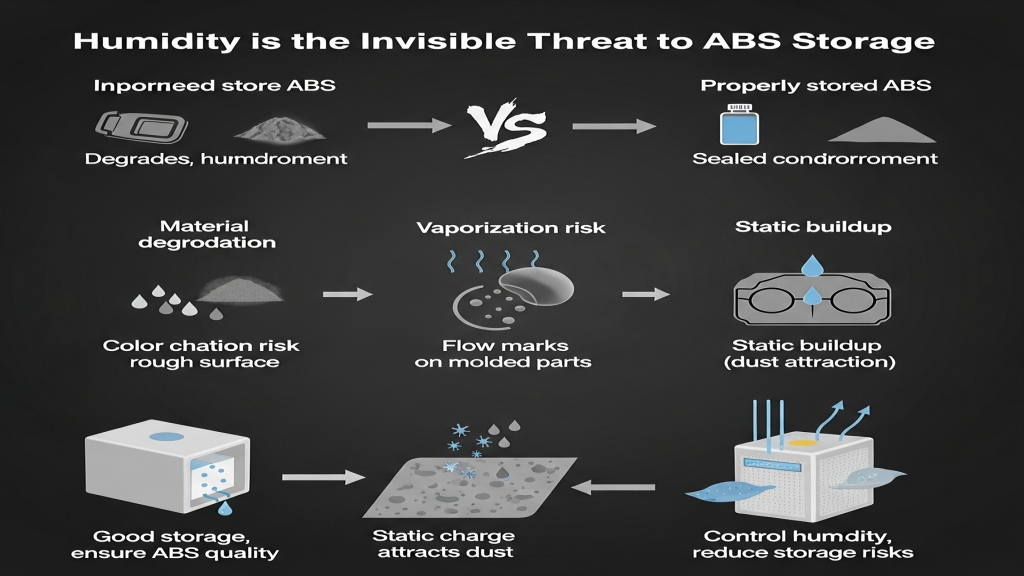
What are the risks of storing ABS in high humidity?
ABS is sensitive to humidity; the longer it is exposed, the higher the moisture content. Unsealed packaging can lead to problematic moisture levels in a short time. Poor storage management is a major source of hidden defects.
- Material degradation: performance declines in humid storage
- Vaporization risks: steam causes flow marks during molding
- Static buildup: attracts dust, leads to contamination
- High storage standards: sealed bins and dry cabinets required
🌫️ Invisible humidity can silently degrade your materials
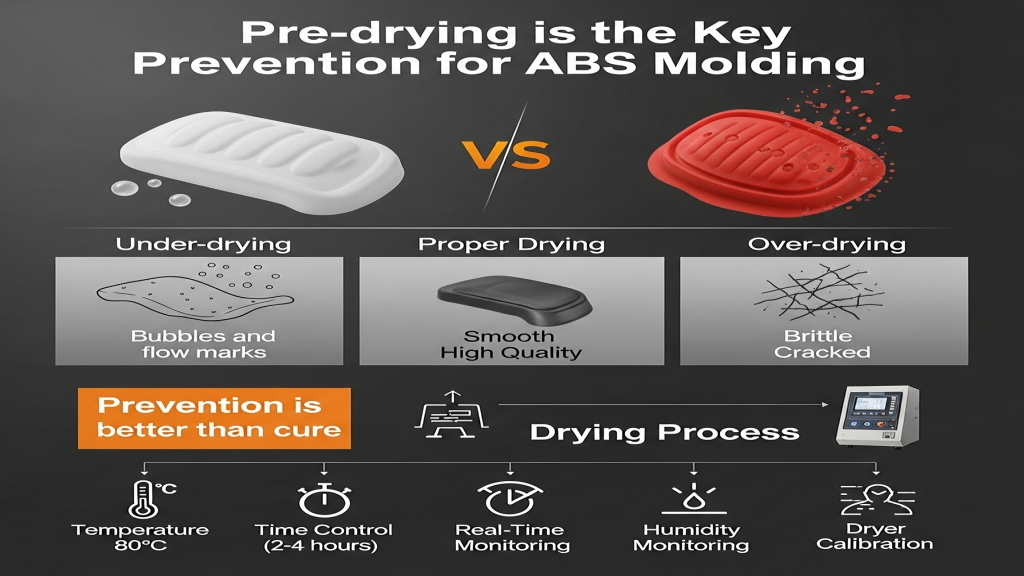
Can pre-drying eliminate the risk?
Pre-drying is essential for ABS molding, effectively lowering moisture with proper time and temperature. But under- or over-drying can be harmful. Accurate drying control directly impacts product stability.
- Recommended drying guide: 80°C for 2–4 hours
- Dryer calibration: ensure constant, reliable heat
- Avoid overdrying: it can make ABS brittle
- Real-time monitoring: moisture absorption happens fast post-exposure
🔥 Drying isn’t a fix—it’s prevention
Water Absorption Comparison of Common Plastics
| Material | Water Abs. (24h) | Drying Need | Typical Use | Defect Risk | Critical Moisture | Process Advice | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | 0.2~0.4 | Required | Auto, Home | Medium | 0.1% | Dry + seal | Medium |
| PC | 0.1~0.3 | High | Lighting, E | High | 0.05% | Vacuum dry | High |
| PP | 0.01 | None | Packaging | Low | N/A | Store normally | Low |
| PA6 | 1.0~1.5 | High | Industrial | Extreme | 0.2% | Low-dew drying | High |
Expansion
ABS is not the only material sensitive to moisture—many engineering plastics share the challenge. Overlooking this issue in production can result in quality fluctuations, returns, or customer claims. A robust drying and storage control system is key to maintaining consistency.
- Drying system integration: real-time moisture monitoring
- Storage-flow control: integrate warehousing with production
- Formulation optimization: try anti-hygroscopic ABS grades
- Mold venting optimization: reduce flow marks from vapor
Conclusion
While ABS has only moderate moisture sensitivity, the risk becomes serious in production scenarios. Each step—from storage to molding—requires strict control. As demand for aesthetics and strength rises, moisture management becomes non-negotiable. A comprehensive moisture control system ensures stable, high-yield production.
For expert assistance in implementing for your production needs, visit our resource center or contact us. Let’s help you scale up your manufacturing with precision and efficiency!