Introduction

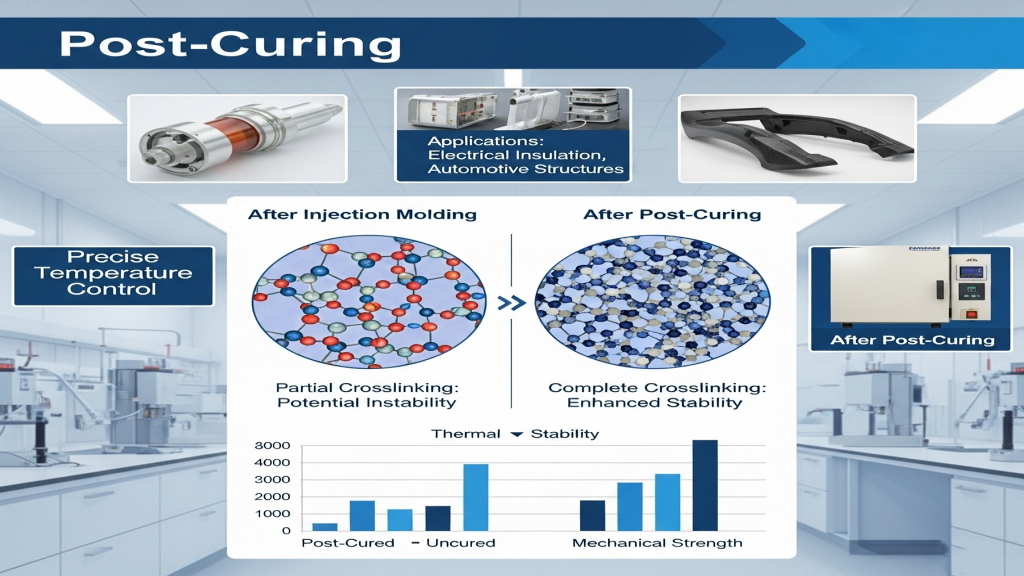
Post-curing is a critical thermal process in the injection molding industry, mainly applied to thermoset plastics and some engineering thermoplastics. It further promotes molecular crosslinking within the material, enhancing thermal stability and dimensional accuracy.This process has a profound impact on the final performance of products, especially in high-reliability industries.
In applications such as electronics, electrical enclosures, and automotive parts, post-curing enhances heat and chemical resistance, preventing deformation and cracking over time. For many high-performance resins, post-curing is essential to unleash their full potential.Incorporating this step before product delivery significantly reduces returns and customer complaints.
Why Do Thermoset Molded Parts Require Post-Curing?

During injection molding, thermoset materials undergo partial crosslinking, but some chemical bonds remain unreacted. Post-curing completes these reactions, improving overall material performance.This reinforcing heat treatment is especially suitable for composite materials like BMC and SMC.
- Improve Thermal Stability: Enhances temperature resistance through complete crosslinking.
- Enhance Structural Integrity: Reduces microcrack formation by densifying internal structure.
- Extend Product Lifespan: Boosts aging resistance and fatigue strength.
- Ensure Industrial Safety: Prevents failure of electrical parts due to thermal expansion or breakdown.
🛠️ Post-curing is the key step from “material qualified” to “product qualified.”
How Does Post-Curing Improve Product Performance?
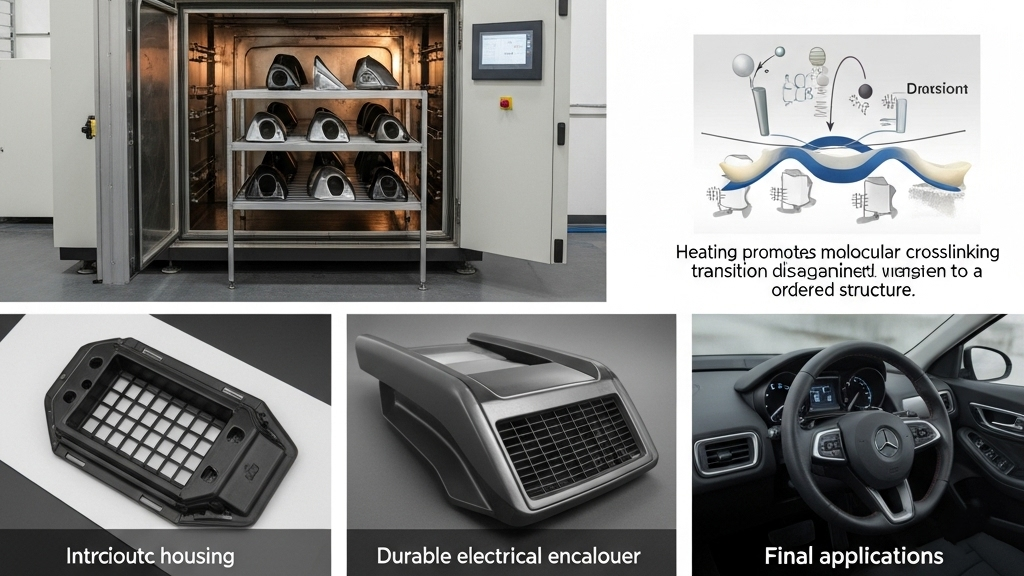

Post-curing not only enhances internal molecular structure but also significantly improves physical properties. For molded parts requiring high strength and precision, it is often indispensable.Post-cured components exhibit superior impact resistance and durability.
- Improve Mechanical Strength: Greater crosslinking results in better compression and tensile performance.
- Increase Heat Deflection Temperature: More resistant to softening or deformation in high-heat environments.
- Improve Dimensional Stability: Prevents shrinkage or expansion during long-term use.
- Boost Chemical Resistance: Withstands exposure to oils and solvents.
🔥 It’s the transition from “usable” to “durable.”
How to Control Post-Curing Conditions for Different Materials?
Different materials require unique time and temperature settings. Epoxy, phenolic, and polyester resin systems must be heated according to their specific curing mechanisms.Proper control can significantly improve batch yield and consistency.
- BMC/SMC Process: Typically cured at 140–180°C for 1–4 hours.
- Epoxy Systems: Recommended gradual heating to avoid thermal shock and cracking.
- Phenolic Materials: Use stepwise heating to release stress steadily.
- Modified Composites: Require catalyst systems for reaction rate control.
📊 Precise control of the curing window ensures production stability.
Post-Curing Process Comparison Table
| Material Type | Temperature | Time | Application Scene | Heat Deflection | Dimensional Stability | Processing Demand | Process Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMC | 160°C | 3 hours | Electrical switch parts | High | High | Medium | High |
| Phenolic | 180°C | 2 hours | Auto interiors, enclosures | Medium | High | High | Medium |
| Epoxy | 150°C | 4 hours | High-voltage insulation | High | High | High | High |
| Modified Polyester | 140°C | 2 hours | Industrial connectors | Medium | Medium | Medium | High |
Is Post-Curing Suitable for All Molded Parts?
Post-curing is mainly used for thermosets or high-performance plastics. General-purpose thermoplastics like PP or PE do not require this treatment. However, for parts needing precision and durability, post-curing significantly boosts performance.Trial runs and comparative data help determine if post-curing should be implemented.
1.Ideal for High-Performance Resins: Such as epoxy, BMC, PPS, etc.
2.Recommended for High-Reliability Products: e.g. insulation or automotive functional parts.
3.Not Needed for Common Thermoplastics: PP, ABS lack a crosslinkable structure.
4.Mold Flow Analysis Recommended: To evaluate heat conduction and residual stress comprehensively.
Conclusion
Post-curing is an essential auxiliary process to enhance injection molded products. It improves mechanical properties and optimizes dimensional stability and appearance. Especially in high-end sectors like automotive and industrial electronics, it plays a crucial role.Well-designed post-curing strategy helps reduce cost and boost competitiveness.
For expert assistance in implementing for your production needs, visit our resource center or contact us. Let’s help you scale up your manufacturing with precision and efficiency!