Introduction
Nylon and polyester exhibit distinct molecular structures in injection molding, directly influencing the choice and optimization of processing techniques. Accurately mastering the physical and chemical properties of materials is the foundation for ensuring production stability and product performance. Through targeted process design, the advantages of materials can be maximized while reducing production defects.
Polyester excels in heat resistance and dimensional stability, while nylon stands out for its toughness and wear resistance. Properly allocating material applications in production can effectively reduce manufacturing costs and enhance market competitiveness.
How to control processing temperature for nylon & polyester?
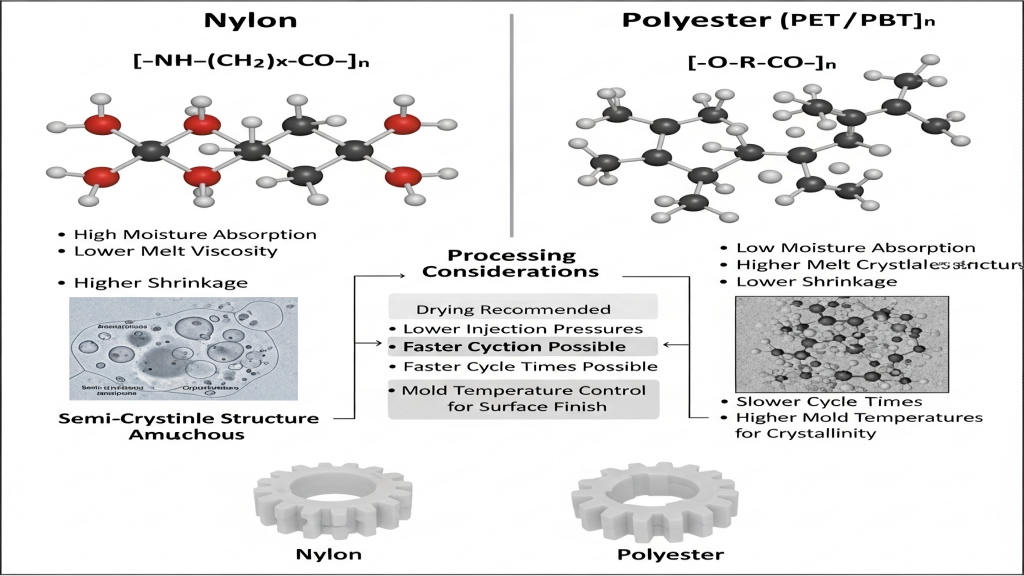
Processing temperature significantly impacts the molecular chain structure of nylon and polyester—too high may cause degradation, while too low may lead to poor flowability. By precisely setting barrel, mold, and hot runner temperatures, stable molding and high surface quality can be achieved. Different materials require temperature control strategies based on their melting points and thermal sensitivity.
- Temperature Curve Optimization: Ensure heating zones and mold temperature are well-coordinated.
- Balanced Heating: Reduce local stress concentration caused by temperature differences.
- Hot Runner Monitoring: Enable real-time temperature feedback and adjustment.
- Degradation Prevention: Avoid high-temperature residence leading to performance loss.
😊 Accurate temperature control is a key factor in improving the consistency of nylon and polyester processing
How to manage moisture for nylon & polyester molding?
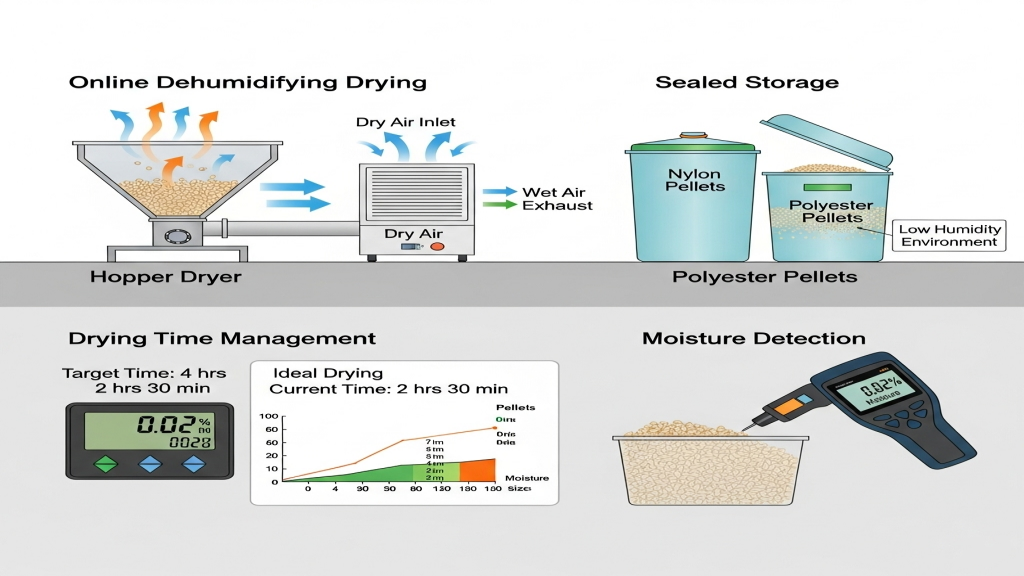
Nylon and polyester require strict drying before processing to prevent moisture-induced decomposition at high temperatures, which may cause bubbles or silver streaks. Using online drying equipment and humidity sensors can significantly reduce molding defects. Each material needs drying temperature and time parameters suited to its properties.
- Online Dehumidifying Drying: Continuously lower material moisture to maintain stable production.
- Sealed Storage: Prevent ambient moisture from entering raw materials during standby.
- Drying Time Management: Ensure complete drying without thermal degradation.
- Moisture Detection: Use sensors for real-time moisture content feedback.
💧 Moisture control is the key to ensuring product appearance and structural integrity
How to improve nylon & polyester flowability in molding?
Flowability determines filling precision in molds, and nylon and polyester differ due to their molecular structures. Adjusting melt temperature, injection speed, and mold gate design can greatly improve filling results. Proper process settings reduce internal stress and warpage risks.
- Runner Design Optimization: Shorten flow paths to reduce pressure loss.
- Injection Speed Matching: Ensure even and fast melt filling.
- Melt Temperature Control: Increase flowability without causing degradation.
- Pressure Curve Adjustment: Lower residual stress inside molded parts.
🚀 Flowability optimization improves molding quality and dimensional accuracy for complex parts
Nylon vs Polyester Processing Performance Comparison
| Performance Item | Nylon Advantage | Polyester Advantage | Process Notes | Application Field |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wear Resistance | High | Medium | Moderate temp control | Gear parts |
| Dimensional Stability | Medium | High | Even mold cooling | Precision housings |
| Moisture Absorption | High | Low | Pre-drying required | Outdoor parts |
| Heat Resistance | Medium | High | Optimized high-temp molding | Electronic parts |
Post-Processing Stabilization
After molding, nylon and polyester parts require post-processing techniques such as annealing, surface coating, or controlled cooling to enhance durability and appearance. Scientific post-processing can significantly extend product lifespan and increase market acceptance. Developing differentiated stabilization methods for each material is key to adding product value.
1.Annealing: Reduce internal stress and prevent deformation.
2.Surface Treatment: Improve wear resistance and aesthetics.
3.Cooling Control: Maintain dimensional stability and prevent warpage.
4.Functional Coatings: Enhance chemical resistance and weather durability.
Conclusion
The process control of nylon and polyester involves precise management of temperature, moisture, and flowability, as well as systematic optimization of post-processing and mold design. Full-process control enables both product performance enhancement and production efficiency improvement. In a competitive market, flexibly adapting to material differences is the core strategy for maintaining competitiveness.
For expert assistance in implementing for your production needs, visit our resource center or contact us. Let’s help you scale up your manufacturing with precision and efficiency!