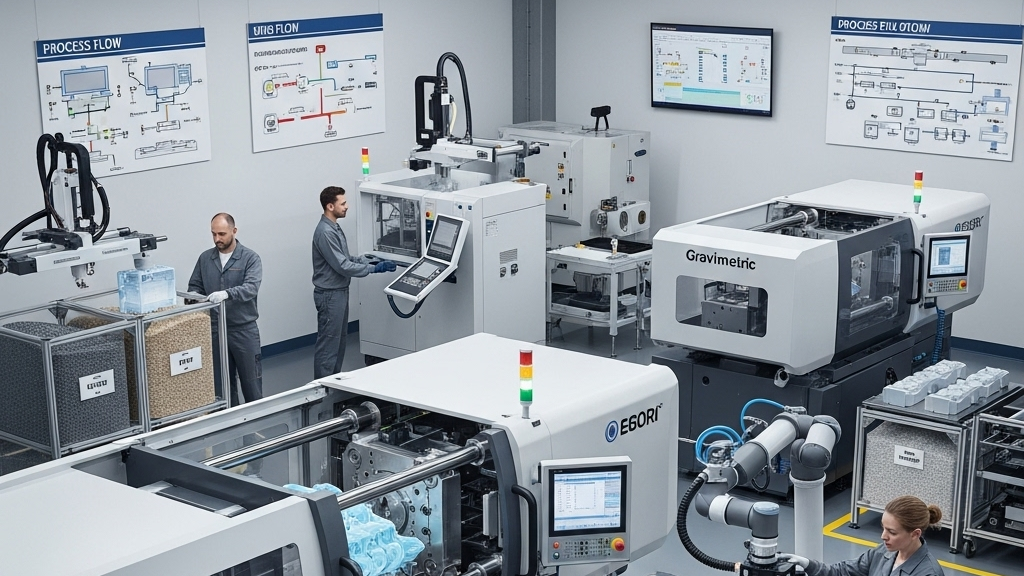
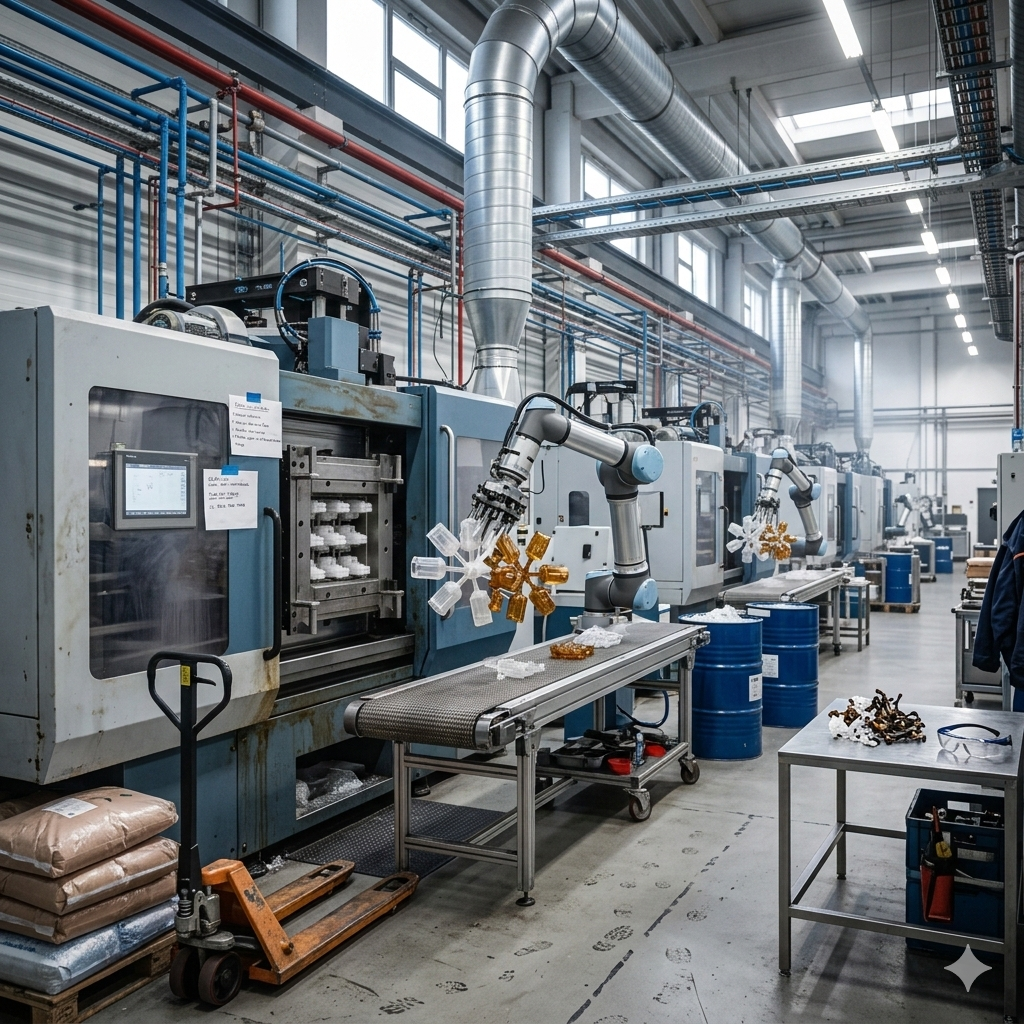
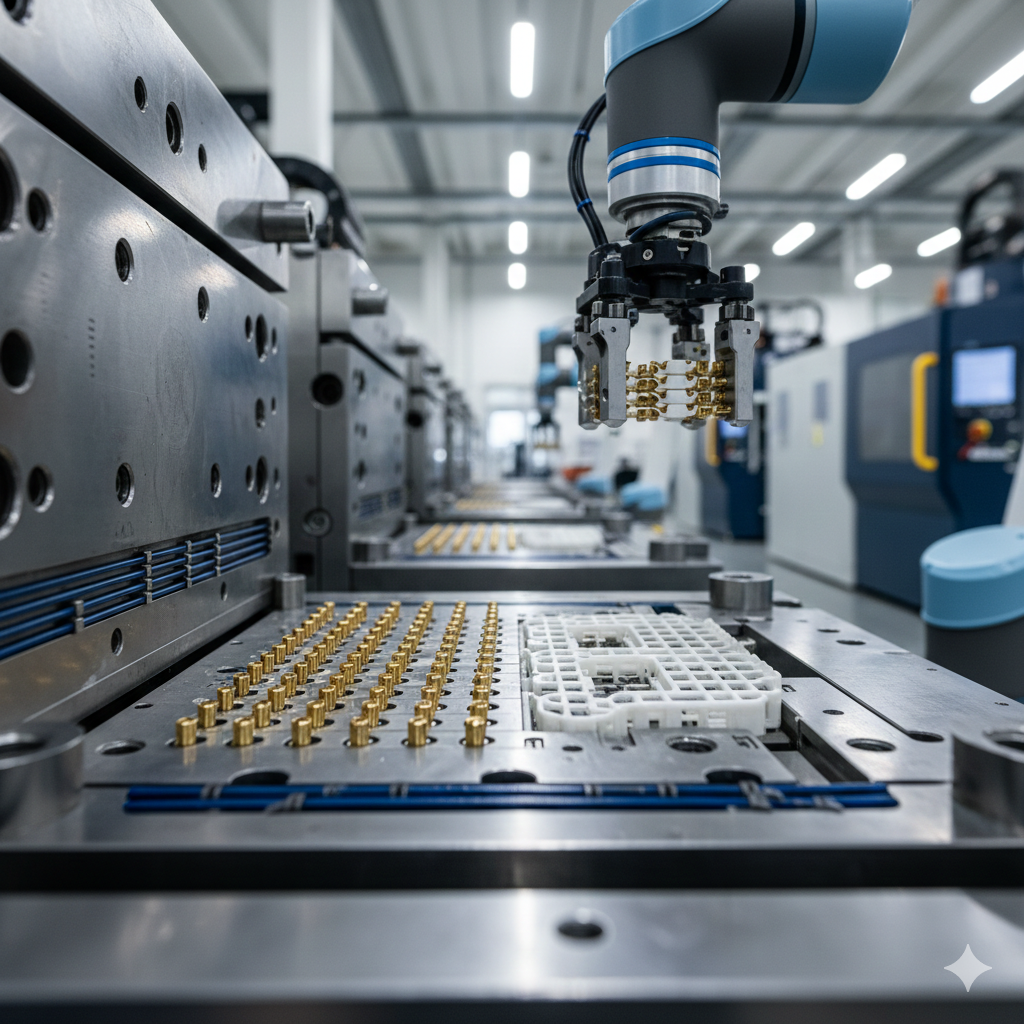
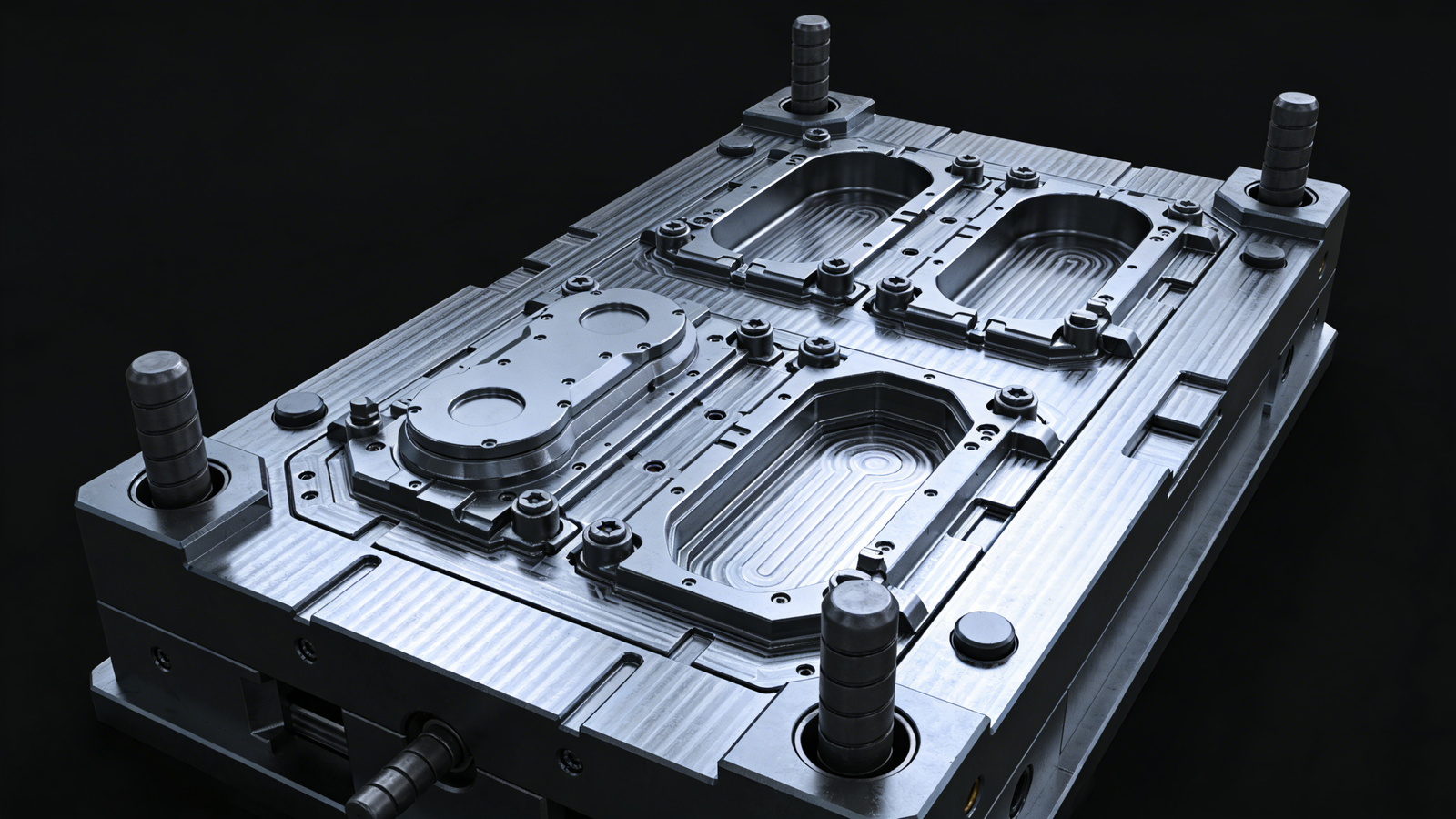
In injection molding, runner design directly determines material efficiency and scrap volume. A well-structured runner not only improves molding quality but also significantly reduces raw material waste.Optimizing the runner system is key to achieving high-efficiency molding.
As lean manufacturing evolves, companies are focusing more on smart runner configurations. Customized designs help reduce cost while maintaining quality. Runner structure impacts the mold system’s overall economic and sustainable performance.
How to choose the right runner type to reduce material waste?
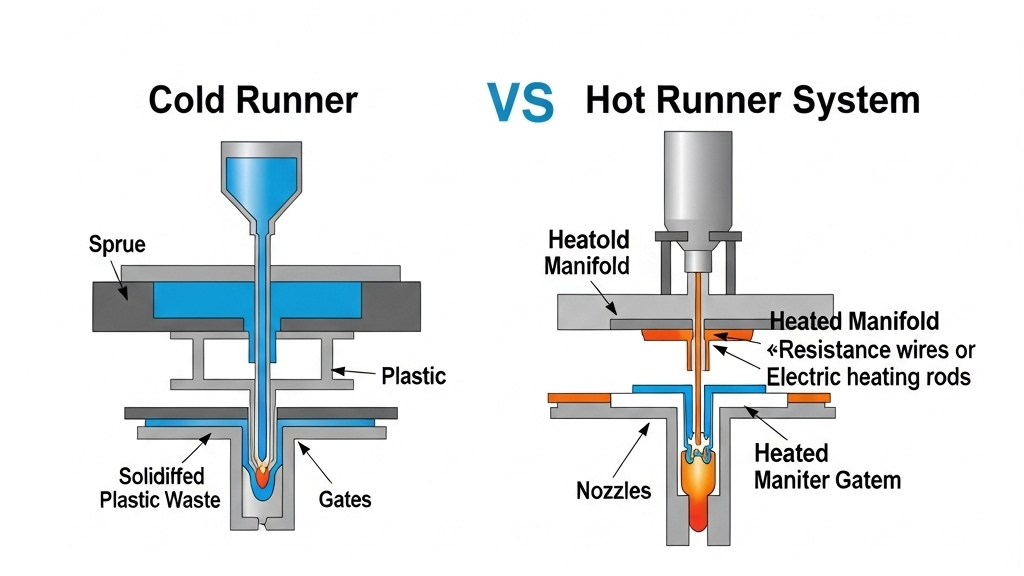
Different product structures and material types require tailored runner choices, whether cold or hot. Proper matching of cross-section and length is vital. Runner diameter and location directly affect scrap volume.
- Benefits of Hot Runner Systems: Reduce waste and enhance part quality.
- Cold Runner Use Cases: Suitable for high melting point and recyclable materials.
- Balanced Flow Design: Prevents uneven flow and waste.
- Short Runners First: Shorter runners mean more efficient material use.
How to arrange runners to optimize flow paths?
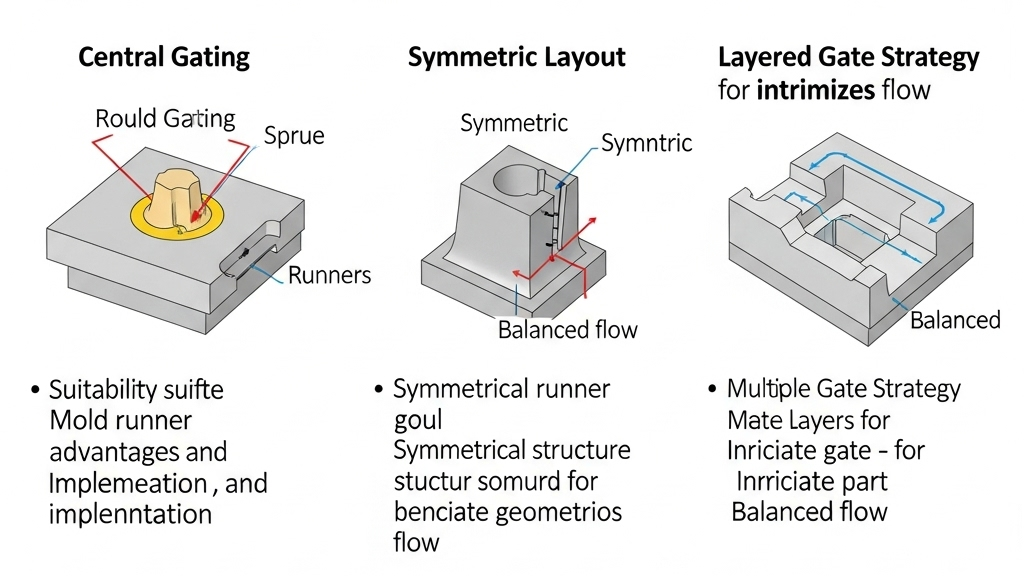
Runner layout should avoid unnecessary crossings and long paths. Ensure the melt takes the shortest path into the cavity. Efficient layout drastically reduces cold slug generation.
- Central Gating Layout: Ensures balanced flow and prevents overpacking.
- Symmetric Layout Principle: Ensures even pressure across cavities.
- Layered Gate Strategy: Improves fill time by distributing melt evenly.
- Shorten Pathways: Saves both time and materials.
How does gate location help reduce material loss?
Strategic gate placement avoids excessive runner length while ensuring part integrity. Gate design is a critical point in controlling material consumption.
- Pin Gate Techniques: Best for small, precise parts to reduce cold slugs.
- Submarine Gates: Concealed entry to reduce trimming and waste.
- Direct Gating: Eliminates parts of runner structures.
- Near-Center Gating: Optimizes flow paths within the cavity.
Comparison of Runner Design Types
| Runner Type | Material Efficiency | Product Scope | Heating Type | Cost | Scrap Level | Recyclability | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold Runner | Medium | General Parts | None | Low | High | Good | Long |
| Hot Runner | High | Precision Parts | Heated Tips | High | Very Low | Poor | Medium |
| Semi-Hot | Relatively High | Small Parts | Partial Heat | Medium | Low | Moderate | Medium |
| Micro Runner | Very High | Thin-Wall Items | High Control | High | Very Low | Poor | Short |
Added Value of Lean Runner Design
High-efficiency runners reduce waste and improve cycle time and equipment utilization. Smart runner solutions drive overall productivity.
1.Higher Output: Shorter fill times and faster cycles.
2.Energy Efficiency: Less heating and cooling required.
3.Automation Friendly: Reduces manual trimming.
4.Eco-Friendly: Less scrap to manage and dispose.
Conclusion
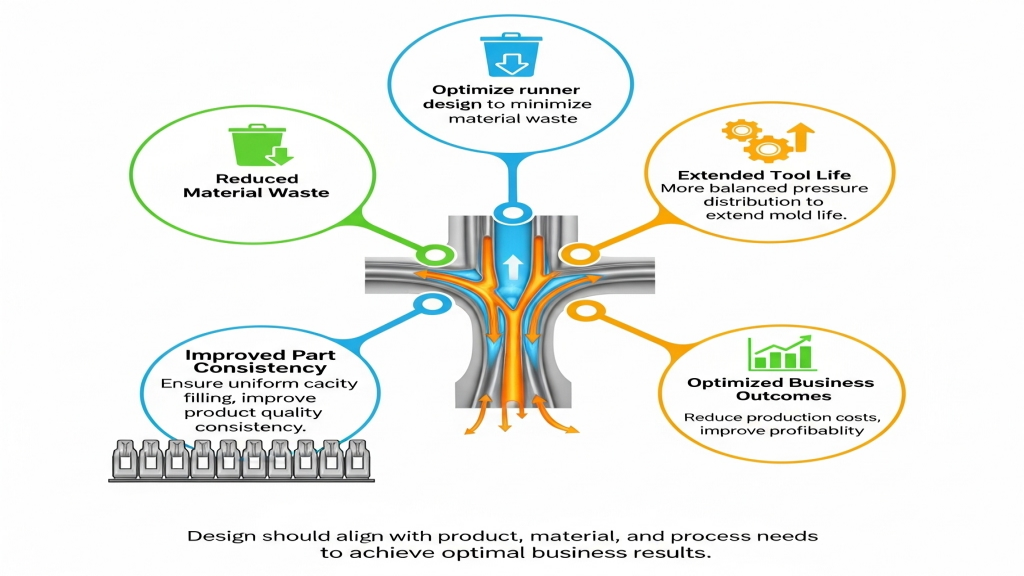
Proper mold runner design not only minimizes material waste but also extends tool life and improves part consistency. Under cost and environmental pressures, optimizing runners is a core strategy for efficient production. Design should align with product, material, and process needs to yield optimal business outcomes.
For expert assistance in implementing for your production needs, visit our resource center or contact us. Let’s help you scale up your manufacturing with precision and efficiency!