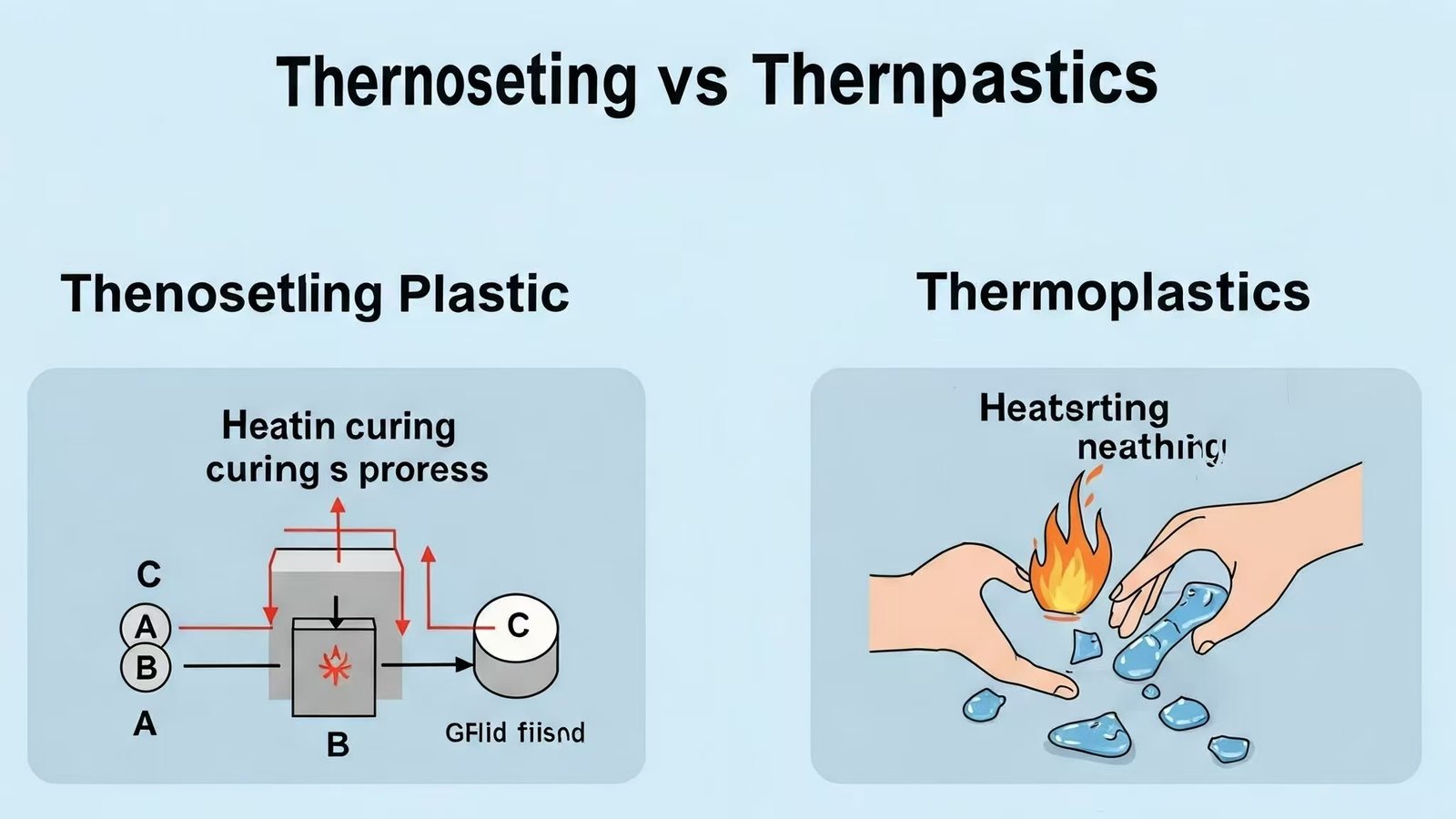
Plastics are divided into two categories thermoplastic and thermoset, and we delve into their microstructure and performance differences. They behave very differently when exposed to heat, and therefore different areas of application.
Thermoplastics are heated and softened, cooled and hardened, and can be repeated. Thermosets are heat-cured and cannot be softened after setting. Distinguishing between them helps us to better choose the right material.
What is the difference in thermal behavior?

Thermoplastics are like candles that can be melted and solidified repeatedly; Whereas, thermosets are like eggs that cannot be restored to their original shape once cooked.
Thermoplastic:
- It softens when heated and hardens when cooled.
- This process can be repeated so that the thermoplastic can be heated and reshaped multiple times.
Thermosets: - After heating, a chemical reaction occurs, solidifies and shapes, forming a cross-linked structure.
- Once cured, reheating will not soften, but will decompose or scorch.
What is the difference in molecular structure?
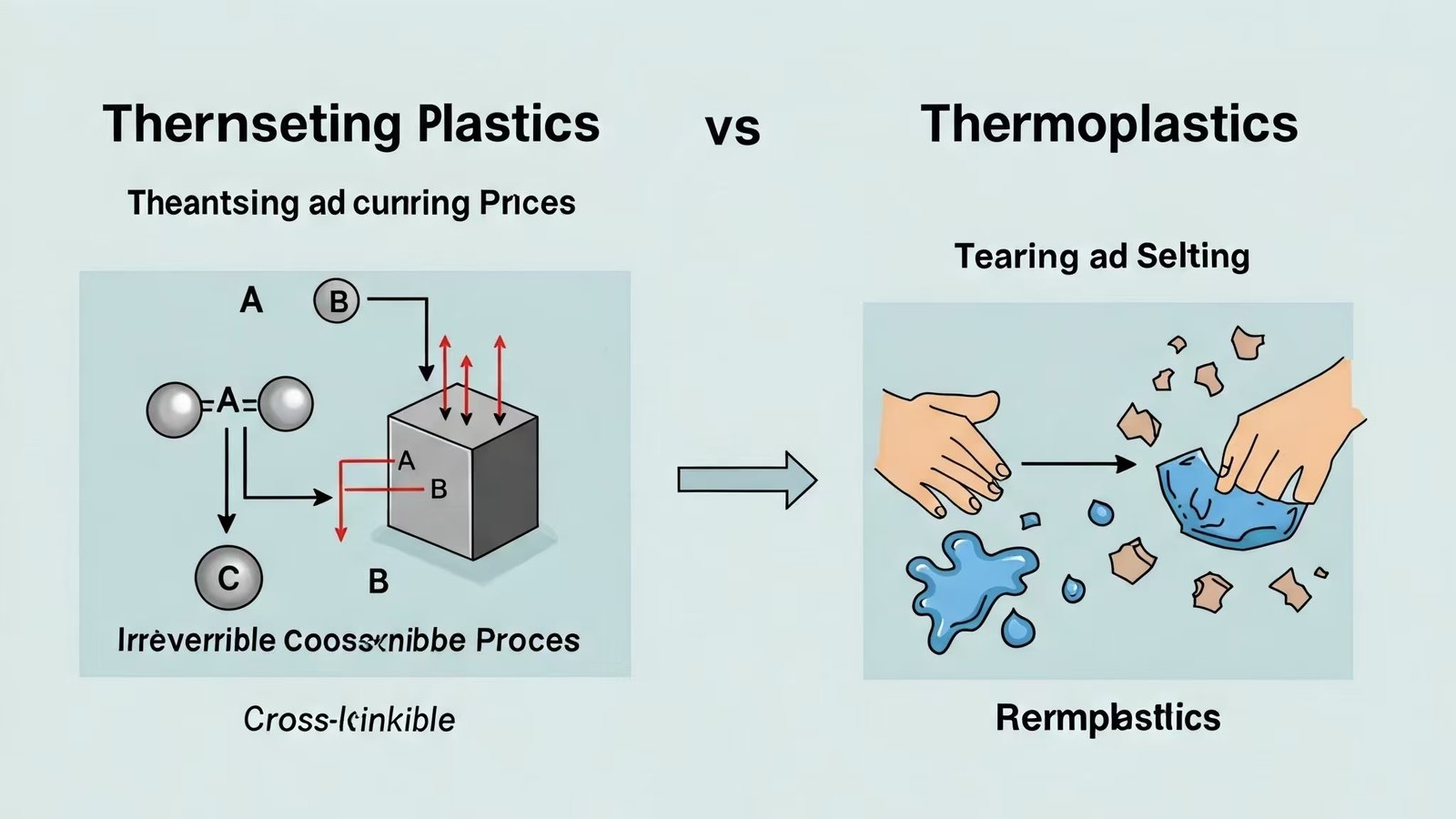
The difference in the properties of thermoplastics and thermosets lies in their molecular structure. This fundamental difference in molecular structure determines how they behave when exposed to heat, and ultimately how they are applied.
Thermoplastic:
- The molecular structure is linear or branched.
- There are no chemical bonds between the molecular chains, so they tend to slide when heated, which is manifested as softening.
Thermosets: - The molecular structure is in the form of a cross-linked network.
- The molecular chains are connected by chemical bonds to form a three-dimensional network structure.
What are the daily applications?

In everyday life, thermoplastics and thermosets are used in a wide range of applications, and their respective characteristics determine their use in different fields
Thermoplastic:
Plastic bottles (PET): Common mineral water bottles, beverage bottles, etc., are widely used in food packaging because they are lightweight, transparent and easy to recycle.
Plastic bags (PE): shopping bags, garbage bags, etc., which are common in supermarkets and stores, are one of the most widely used plastic products in daily life because of their low cost and easy production.
Thermosets:
Electrical switch shell (phenolic resin): Because of its excellent insulation and heat resistance, it is often used to make electrical switches, sockets, etc., to ensure the safety of electricity.
Kitchen tableware (melamine resin): Melamine tableware, because of its drop resistance, high temperature resistance, widely used in the catering industry, and households.
Characteristics and use analysis
| Type of material | Common materials | Main uses | Common processing techniques | Circular environmental features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| thermoplastic | ||||
| Polyethylene (PE) | HDPE (High Density Polyethylene) | Bags, caps, pipes, containers | Extrusion, blow molding, injection molding | It can be recycled, but it degrades slowly and needs to be sorted and recycled |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Homopolymer PP, copolymer PP | Food containers, car parts, woven bags | Injection molding, extrusion, blow molding | It is recyclable, has good heat resistance, is conducive to cleaning, and has a high recycling value |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) | PVC Rigid PVC, soft PVC | Pipes, profiles, wires and cables, artificial leather | Extrusion, calendering, injection molding | It is difficult to recover, contains chlorine, and incineration produces harmful gases, so the use should be reduced |
| Thermosets | ||||
| Phenolic resin | Phenolic molding compounds, phenolic laminates | Electrical components, insulation, plywood | Molding, laminating, injection molding | It is difficult to recycle, cannot be remodeled, and it is difficult to dispose of waste |
| epoxy resin | Liquid epoxy resin, solid epoxy resin | Electronic packaging, coatings, composites | Pouring, coating, laminating | It is difficult to recycle, and the recycling of composite materials is complex, which is more polluting to the environment |
| Unsaturated polyester resin | General unsaturated polyester, FRP resin | FRP products, artificial stone, coatings | Molding, pouring, laminating | It is difficult to recycle, and it is difficult to recycle FRP and needs to be professionally treated |
Balance between product and environmental protection
The balance between production and environmental protection is an important challenge facing society today. It involves finding a sustainable balance between economic development and environmental protection.
1.Sustainable development: Sustainable development requires taking into account the needs of present and future generations, and achieving economic, social and environmental harmony.
2.The contradiction between production and the environment: the traditional production mode can easily lead to excessive consumption of resources and environmental pollution, which will damage development in the long run.
3.Ways to achieve balance: Achieve a balance between production and environmental protection through technological innovation, policy guidance, corporate responsibility and public participation.
4.Why it matters: Balancing production and environmental protection helps protect the ecological environment, promote sustainable economic development, and ensure social equity.
conclusion
The balance between production and environmental protection is not a simple choice, through scientific product selection, efficient material recycling and active environmental protection actions, we can achieve the sustainable use of plastics and protect our planet.
For expert assistance in implementing for your production needs, visit our resource center or contact us. Let’s help you scale up your manufacturing with precision and efficiency!







